What do the API invocation metrics provided by Anypoint Platform provide?
A.
ROI metrics from APIs that can be directly shared with business users
B.
Measurements of the effectiveness of the application network based on the level of reuse
C.
Data on past API invocations to help identify anomalies and usage patterns across various APIs
D.
Proactive identification of likely future policy violations that exceed a given threat
threshold
Data on past API invocations to help identify anomalies and usage patterns across various APIs
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Data on past API invocations to help identify anomalies and usage
patterns across various APIs
*****************************************
API Invocation metrics provided by Anypoint Platform:
>> Does NOT provide any Return Of Investment (ROI) related information. So the option
suggesting it is OUT.
>> Does NOT provide any information w.r.t how APIs are reused, whether there is effective
usage of APIs or not etc...
>> Does NOT prodive any prediction information as such to help us proactively identify any
future policy violations.
So, the kind of data/information we can get from such metrics is on past API invocations to
help identify anomalies and usage patterns across various APIs.
Reference:
https://usermanual.wiki/Document/APAAppNetstudentManual02may2018.991784750.pdf
When using CloudHub with the Shared Load Balancer, what is managed EXCLUSIVELY
by the API implementation (the Mule application) and NOT by Anypoint Platform?
A.
The assignment of each HTTP request to a particular CloudHub worker
B.
The logging configuration that enables log entries to be visible in Runtime Manager
C.
The SSL certificates used by the API implementation to expose HTTPS endpoints
D.
The number of DNS entries allocated to the API implementation
The SSL certificates used by the API implementation to expose HTTPS endpoints
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: The SSL certificates used by the API implementation to expose HTTPS
endpoints
*****************************************
>> The assignment of each HTTP request to a particular CloudHub worker is taken care by
Anypoint Platform itself. We need not manage it explicitly in the API implementation and in
fact we CANNOT manage it in the API implementation.
>> The logging configuration that enables log entries to be visible in Runtime Manager is
ALWAYS managed in the API implementation and NOT just for SLB. So this is not
something we do EXCLUSIVELY when using SLB.
>> We DO NOT manage the number of DNS entries allocated to the API implementation
inside the code. Anypoint Platform takes care of this.
It is the SSL certificates used by the API implementation to expose HTTPS endpoints that
is to be managed EXCLUSIVELY by the API implementation. Anypoint Platform does NOT
do this when using SLBs.
The implementation of a Process API must change.What is a valid approach that minimizes the impact of this change on API clients?
A.
Update the RAML definition of the current Process API and notify API client developers
by sending them links to the updated RAML definition
B.
Postpone changes until API consumers acknowledge they are ready to migrate to a new
Process API or API version
C.
Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that whenever
possible, the Process API's RAML definition remains unchanged
D.
Implement the Process API changes in a new API implementation, and have the old API
implementation return an HTTP status code 301 - Moved Permanently to inform API clients
they should be calling the new API implementation
Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that whenever
possible, the Process API's RAML definition remains unchanged
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that,
whenever possible, the Process API’s RAML definition remains unchanged.
*****************************************
Key requirement in the question is:
>> Approach that minimizes the impact of this change on API clients
Based on above:
>> Updating the RAML definition would possibly impact the API clients if the changes
require any thing mandatory from client side. So, one should try to avoid doing that until
really necessary.
>> Implementing the changes as a completely different API and then redirectly the clients
with 3xx status code is really upsetting design and heavily impacts the API clients.
>> Organisations and IT cannot simply postpone the changes required until all API
consumers acknowledge they are ready to migrate to a new Process API or API version.
This is unrealistic and not possible.
The best way to handle the changes always is to implement required changes to the API
implementations so that, whenever possible, the API’s RAML definition remains
unchanged.
What should be ensured before sharing an API through a public Anypoint Exchange portal?
A.
The visibility level of the API instances of that API that need to be publicly accessible should be set to public visibility
B.
The users needing access to the API should be added to the appropriate role in
Anypoint Platform
C.
The API should be functional with at least an initial implementation deployed and accessible for users to interact with
D.
The API should be secured using one of the supported authentication/authorization mechanisms to ensure that data is not compromised
The visibility level of the API instances of that API that need to be publicly accessible should be set to public visibility
Explanation: Explanation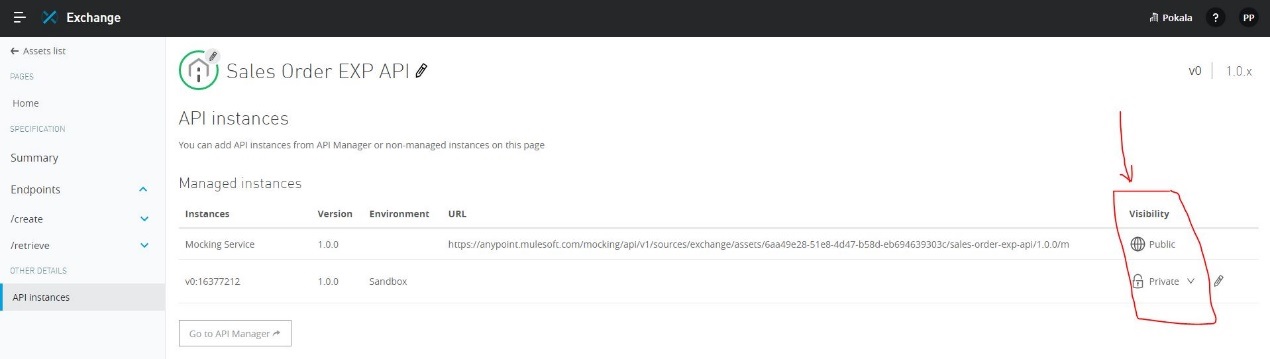
4 Production environment is running on a dedicated Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) on CloudHub 1,0, and the security team guidelines clearly state no traffic on HTTP. Which two options support these security guidelines?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
E. Option E
What are 4 important Platform Capabilities offered by Anypoint Platform?
A.
API Versioning, API Runtime Execution and Hosting, API Invocation, API Consumer Engagement
B.
API Design and Development, API Runtime Execution and Hosting, API Versioning, API
Deprecation
C.
API Design and Development, API Runtime Execution and Hosting, API Operations and
Management, API Consumer Engagement
D.
API Design and Development, API Deprecation, API Versioning, API Consumer
Engagement
API Design and Development, API Runtime Execution and Hosting, API Operations and
Management, API Consumer Engagement
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: API Design and Development, API Runtime Execution and Hosting, API
Operations and Management, API Consumer Engagement
*****************************************
>> API Design and Development - Anypoint Studio, Anypoint Design Center, Anypoint
Connectors
>> API Runtime Execution and Hosting - Mule Runtimes, CloudHub, Runtime Services
>> API Operations and Management - Anypoint API Manager, Anypoint Exchange
>> API Consumer Management - API Contracts, Public Portals, Anypoint Exchange, API
Notebooks
Refer to the exhibit. An organization needs to enable access to their customer data from
both a mobile app and a web application, which each need access to common fields as
well as certain unique fields.
The data is available partially in a database and partially in a 3rd-party CRM system.
What APIs should be created to best fit these design requirements?
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option C
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Separate Experience APIs for the mobile and web app, but a common
Process API that invokes separate System APIs created for the database and CRM system
*****************************************
As per MuleSoft's API-led connectivity:
>> Experience APIs should be built as per each consumer needs and their experience.
>> Process APIs should contain all the orchestration logic to achieve the business
functionality.
>> System APIs should be built for each backend system to unlock their data.
Reference: https://blogs.mulesoft.com/dev/api-dev/what-is-api-led-connectivity
An organization is implementing a Quote of the Day API that caches today's quote.
What scenario can use the GoudHub Object Store via the Object Store connector to persist
the cache's state?
A.
When there are three CloudHub deployments of the API implementation to three
separate CloudHub regions that must share the cache state
B.
When there are two CloudHub deployments of the API implementation by two Anypoint
Platform business groups to the same CloudHub region that must share the cache state
C.
When there is one deployment of the API implementation to CloudHub and anottV
deployment to a customer-hosted Mule runtime that must share the cache state
D.
When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three CloudHub
workers that must share the cache state
When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three CloudHub
workers that must share the cache state
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to
three CloudHub workers that must share the cache state.
*****************************************
Key details in the scenario:
>> Use the CloudHub Object Store via the Object Store connector
Considering above details:
>> CloudHub Object Stores have one-to-one relationship with CloudHub Mule Applications.
>> We CANNOT use an application's CloudHub Object Store to be shared among multiple
Mule applications running in different Regions or Business Groups or Customer-hosted
Mule Runtimes by using Object Store connector.
>> If it is really necessary and very badly needed, then Anypoint Platform supports a way
by allowing access to CloudHub Object Store of another application using Object Store
REST API. But NOT using Object Store connector.
So, the only scenario where we can use the CloudHub Object Store via the Object Store
connector to persist the cache’s state is when there is one CloudHub deployment of the
API implementation to multiple CloudHub workers that must share the cache state
| Page 5 out of 19 Pages |
| Mulesoft MCPA-Level-1 Exam Questions Home | Previous |