What Mule application deployment scenario requires using Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition or Anypoint Platform for Pivotal Cloud Foundry?
A.
When it Is required to make ALL applications highly available across multiple data centers
B.
When it is required that ALL APIs are private and NOT exposed to the public cloud
C.
When regulatory requirements mandate on-premises processing of EVERY data item, including meta-data
D.
When ALL backend systems in the application network are deployed in the
organization's intranet
When regulatory requirements mandate on-premises processing of EVERY data item, including meta-data
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: When regulatory requirements mandate on-premises processing of EVERY data item, including meta-data.
*****************************************
We need NOT require to use Anypoint Platform PCE or PCF for the below. So these
options are OUT.
>> We can make ALL applications highly available across multiple data centers using
CloudHub too.
>> We can use Anypoint VPN and tunneling from CloudHub to connect to ALL backend
systems in the application network that are deployed in the organization's intranet.
>> We can use Anypoint VPC and Firewall Rules to make ALL APIs private and NOT
exposed to the public cloud.
Only valid reason in the given options that requires to use Anypoint Platform PCE/ PCF is -
When regulatory requirements mandate on-premises processing of EVERY data item,
including meta-data
An Order API triggers a sequence of other API calls to look up details of an order's items in
a back-end inventory database. The Order API calls the OrderItems process API, which
calls the Inventory system API. The Inventory system API performs database operations in
the back-end inventory database.
The network connection between the Inventory system API and the database is known to
be unreliable and hang at unpredictable times.
Where should a two-second timeout be configured in the API processing sequence so that
the Order API never waits more than two seconds for a response from the Orderltems
process API?
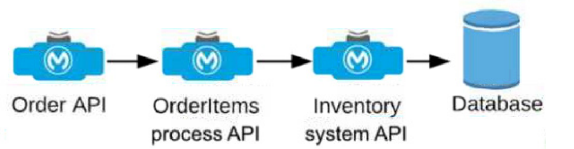
A. In the Orderltems process API implementation
B. In the Order API implementation
C. In the Inventory system API implementation
D. In the inventory database
A Mule application exposes an HTTPS endpoint and is deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud. All traffic to that Mule application must stay inside the AWS VPC. To what TCP port do API invocations to that Mule application need to be sent?
A.
443
B.
8081
C.
8091
D.
8082
8082
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: 8082
*****************************************
>> 8091 and 8092 ports are to be used when keeping your HTTP and HTTPS app private
to the LOCAL VPC respectively.
>> Above TWO ports are not for Shared AWS VPC/ Shared Worker Cloud.
>> 8081 is to be used when exposing your HTTP endpoint app to the internet through
Shared LB
>> 8082 is to be used when exposing your HTTPS endpoint app to the internet through
Shared LB
So, API invocations should be sent to port 8082 when calling this HTTPS based app.
References:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-manager/cloudhub-networking-guide
https://help.mulesoft.com/s/article/Configure-Cloudhub-Application-to-Send-a-HTTPSRequest-
Directly-to-Another-Cloudhub-Application
https://help.mulesoft.com/s/question/0D52T00004mXXULSA4/multiple-http-listerners-oncloudhub-
one-with-port-9090
A new upstream API Is being designed to offer an SLA of 500 ms median and 800 ms
maximum (99th percentile) response time. The corresponding API implementation needs to
sequentially invoke 3 downstream APIs of very similar complexity.
The first of these downstream APIs offers the following SLA for its response time: median:
100 ms, 80th percentile: 500 ms, 95th percentile: 1000 ms.
If possible, how can a timeout be set in the upstream API for the invocation of the first
downstream API to meet the new upstream API's desired SLA?
A.
Set a timeout of 50 ms; this times out more invocations of that API but gives additional
room for retries
B.
Set a timeout of 100 ms; that leaves 400 ms for the other two downstream APIs to complete
C.
No timeout is possible to meet the upstream API's desired SLA; a different SLA must be
negotiated with the first downstream API or invoke an alternative API
D.
Do not set a timeout; the Invocation of this API Is mandatory and so we must wait until it
responds
Set a timeout of 100 ms; that leaves 400 ms for the other two downstream APIs to complete
Explanation:
Explanation
Correct Answer: Set a timeout of 100ms; that leaves 400ms for other two downstream APIs
to complete
*****************************************
Key details to take from the given scenario:
>> Upstream API's designed SLA is 500ms (median). Lets ignore maximum SLA response
times.
>> This API calls 3 downstream APIs sequentially and all these are of similar complexity.
>> The first downstream API is offering median SLA of 100ms, 80th percentile: 500ms;
95th percentile: 1000ms.
Based on the above details:
>> We can rule out the option which is suggesting to set 50ms timeout. Because, if the
median SLA itself being offered is 100ms then most of the calls are going to timeout and
time gets wasted in retried them and eventually gets exhausted with all retries. Even if
some retries gets successful, the remaining time wont leave enough room for 2nd and 3rd
downstream APIs to respond within time.
>> The option suggesting to NOT set a timeout as the invocation of this API is mandatory
and so we must wait until it responds is silly. As not setting time out would go against the
good implementation pattern and moreover if the first API is not responding within its
offered median SLA 100ms then most probably it would either respond in 500ms (80th
percentile) or 1000ms (95th percentile). In BOTH cases, getting a successful response
from 1st downstream API does NO GOOD because already by this time the Upstream API
SLA of 500 ms is breached. There is no time left to call 2nd and 3rd downstream APIs.
>> It is NOT true that no timeout is possible to meet the upstream APIs desired SLA.
As 1st downstream API is offering its median SLA of 100ms, it means MOST of the time we
would get the responses within that time. So, setting a timeout of 100ms would be ideal for
MOST calls as it leaves enough room of 400ms for remaining 2 downstream API calls.
A large company wants to implement IT infrastructure in its own data center, based on the corporate IT policy requirements that data and metadata reside locally. Which combination of Mule control plane and Mule runtime plane(s) meets the requirements?
A. Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition for the control plane and the MuleSoft-hosted runtime plane
B. The MuleSoft-hosted control plane and Anypoint Runtime Fabric for the runtime plane
C. The MuleSoft-hosted control plane and customer-hosted Mule runtimes for the runtime plane
D. Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition for the control plane and customer-hosted Mule runtimes for the runtime plane
Explanation:
Which APIs can be used with DataGraph to create a unified schema?
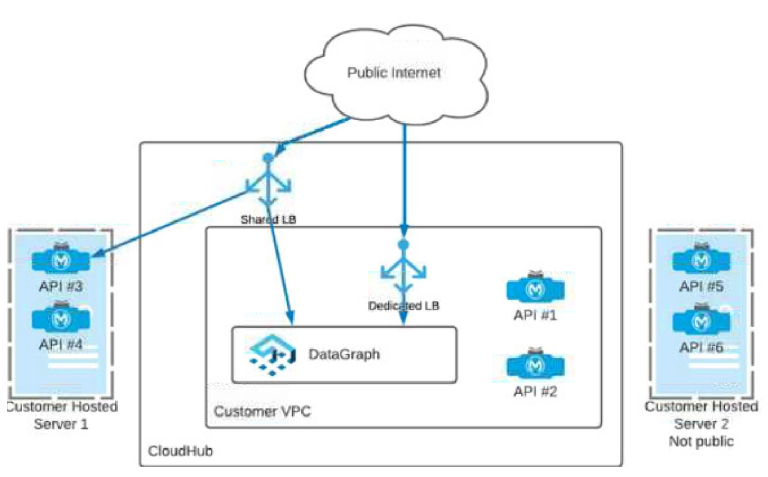
A. APIs 1, 3, 5
B. APIs 2, 4 ,6
C. APIs 1, 2, s5, 6
D. APIs 1, 2, 3, 4
Explanation:
To create a unified schema in MuleSoft's DataGraph, APIs must be exposed
in a way that allows DataGraph to pull and consolidate data from these APIs into a single
schema accessible to consumers. DataGraph provides a federated approach, combining
multiple APIs to form a single, unified API endpoint.
In this setup:
APIs 1, 2, 3, and 4 are suitable candidates for DataGraph because they are hosted
within the Customer VPC on CloudHub and are accessible either through a
Shared Load Balancer (LB) or a Dedicated Load Balancer (DLB). Both of these
load balancers provide public access, which is a necessary condition for
DataGraph as it must access the APIs to aggregate data.
APIs 5 and 6 are hosted on Customer Hosted Server 2, which is explicitly marked
as "Not public". Since DataGraph requires API access through a publicly
reachable endpoint to aggregate them into a unified schema, APIs 5 and 6 cannot
be used with DataGraph in this configuration.
APIs 3 and 4 on Customer Hosted Server 1 appear accessible through a Shared
LB, implying public accessibility that meets DataGraph’s requirements.
By combining APIs 1, 2, 3, and 4 within DataGraph, you can create a unified schema that
enables clients to query data seamlessly from all these APIs as if it were from a single
source.
This setup allows for efficient data retrieval and can simplify API consumption by reducing
the need to call multiple APIs individually, thus optimizing performance and developer
experience.
When could the API data model of a System API reasonably mimic the data model
exposed by the corresponding backend system, with minimal improvements over the
backend system's data model?
A.
When there is an existing Enterprise Data Model widely used across the organization
B.
When the System API can be assigned to a bounded context with a corresponding data
model
C.
When a pragmatic approach with only limited isolation from the backend system is deemed appropriate
D.
When the corresponding backend system is expected to be replaced in the near future
When a pragmatic approach with only limited isolation from the backend system is deemed appropriate
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: When a pragmatic approach with only limited isolation from the backend
system is deemed appropriate.
*****************************************
General guidance w.r.t choosing Data Models:
>> If an Enterprise Data Model is in use then the API data model of System APIs should
make use of data types from that Enterprise Data Model and the corresponding API
implementation should translate between these data types from the Enterprise Data Model
and the native data model of the backend system.
>> If no Enterprise Data Model is in use then each System API should be assigned to a
Bounded Context, the API data model of System APIs should make use of data types from
the corresponding Bounded Context Data Model and the corresponding API
implementation should translate between these data types from the Bounded Context Data
Model and the native data model of the backend system. In this scenario, the data types in
the Bounded Context Data Model are defined purely in terms of their business
characteristics and are typically not related to the native data model of the backend system.
In other words, the translation effort may be significant.
>> If no Enterprise Data Model is in use, and the definition of a clean Bounded Context
Data Model is considered too much effort, then the API data model of System APIs should
make use of data types that approximately mirror those from the backend system, same
semantics and naming as backend system, lightly sanitized, expose all fields needed for
the given System API’s functionality, but not significantly more and making good use of
REST conventions.
The latter approach, i.e., exposing in System APIs an API data model that basically mirrors
that of the backend system, does not provide satisfactory isolation from backend systems
through the System API tier on its own. In particular, it will typically not be possible to
"swap out" a backend system without significantly changing all System APIs in front of that
backend system and therefore the API implementations of all Process APIs that depend on
those System APIs! This is so because it is not desirable to prolong the life of a previous
backend system’s data model in the form of the API data model of System APIs that now
front a new backend system. The API data models of System APIs following this approach
must therefore change when the backend system is replaced.
On the other hand:
>> It is a very pragmatic approach that adds comparatively little overhead over accessing
the backend system directly
>> Isolates API clients from intricacies of the backend system outside the data model
(protocol, authentication, connection pooling, network address, …)
>> Allows the usual API policies to be applied to System APIs
>> Makes the API data model for interacting with the backend system explicit and visible,
by exposing it in the RAML definitions of the System APIs
>> Further isolation from the backend system data model does occur in the API
The responses to some HTTP requests can be cached depending on the HTTP verb used
in the request. According to the HTTP specification, for what HTTP verbs is this safe to do?
A.
PUT, POST, DELETE
B.
GET, HEAD, POST
C.
GET, PUT, OPTIONS
D.
GET, OPTIONS, HEAD
GET, OPTIONS, HEAD
| Page 1 out of 19 Pages |