A Mule flow has three Set Variable transformers. What global data structure can be used to
access the variables?
A.
Mule event attributes
B.
Mule event message
C.
Mule application properties
D.
Mule event
Mule event
Refer to the exhibits.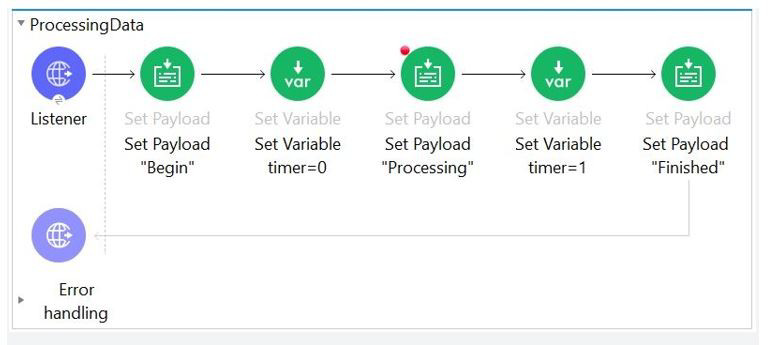
The Mule Application is being debugged in Anypoint Studio and stops at breakpoint. What
is the value of payload displayed in debugger at this breakpoint?
A. Processing
B. Begin
C. Finished
Refer to the exhibit.

What is the response to a web client request tohttp://localhost:8081?
A.
After
B.
before
C.
Validation Error
D.
null
Validation Error
A company has an API to manage departments, with each department identified by a
unique deptld. The API was built with RAML according to MuleSoft best practices.
What is valid RAML to specify a method to update the details for a specific department?
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
What is the difference between a subflow and a sync flow?
A. No difference
B. Subflow has no error handling of its own and sync flow does
C. Sync flow has no error handling of its own and subflow does
D. Subflow is synchronous and sync flow is asynchronous
Explanation:
Correct answer is Subflow has no error handling implementation where as sync flow has Subflow:
A subflow processes messages synchronously (relative to the flow that triggered its
execution) and always inherits both the processing strategy and exception strategy
employed by the triggering flow. While a subflow is running, processing on the triggering
flow pauses, then resumes only after the subflow completes its processing and hands the
message back to the triggering flow.
Synchronous Flow:
A synchronous flow, like a subflow, processes messages synchronously (relative to the
flow that triggered its execution). While a synchronous flow is running, processing on the
triggering flow pauses, then resumes only after the synchronous flow completes its
processing and hands the message back to the triggering flow. However, unlike a subflow,
this type of flow does not inherit processing or exception strategies from the triggering flow.
This type of flow processes messages along a single thread, which is ideally suited to
transactional processing.
Refer to the exhibits.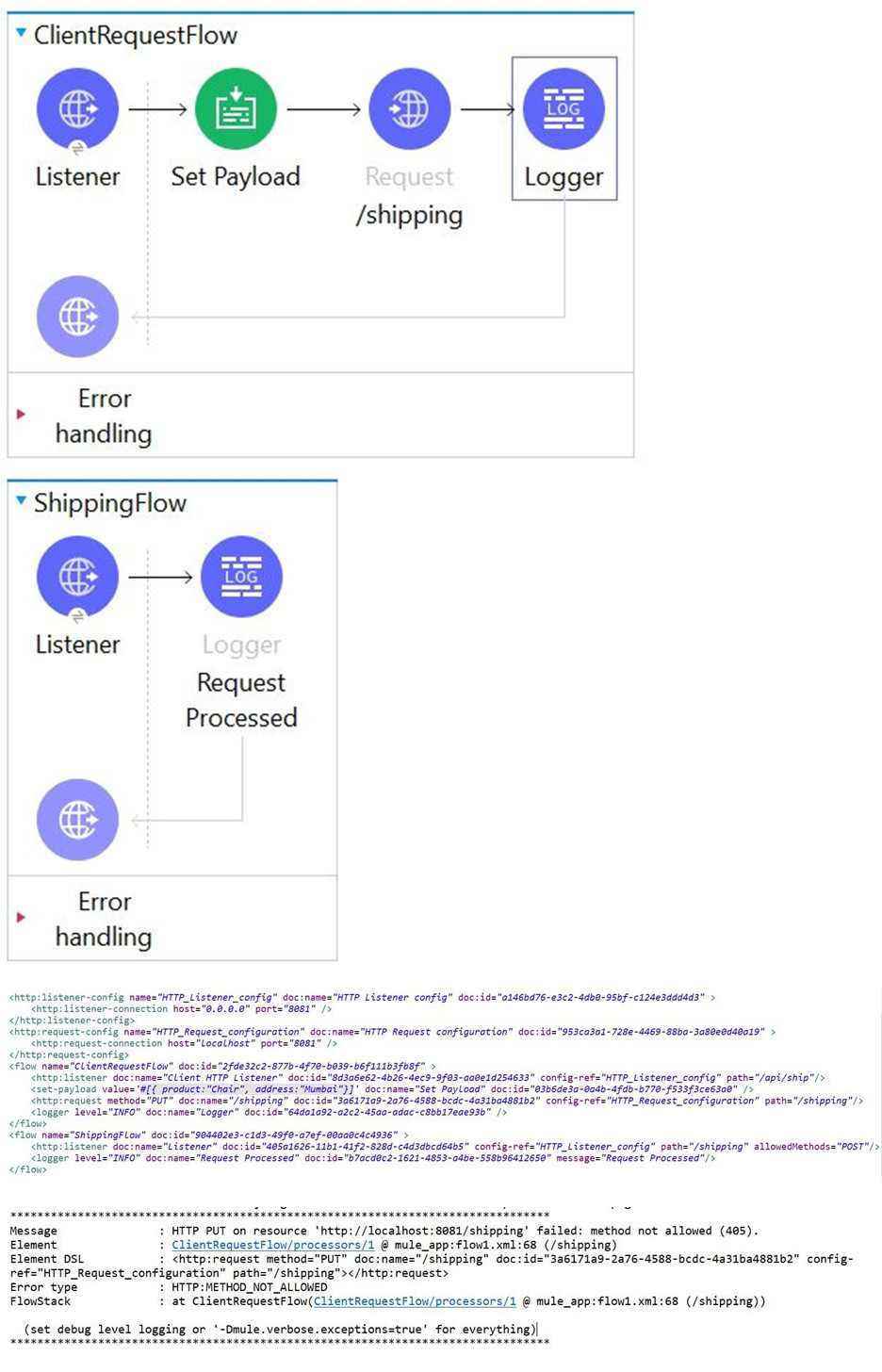
Client sends the request to ClientRequestFlow which calls
ShippingFlow using HTTP Request activity.
During E2E testing it is found that that HTTP:METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED error is thrown
whenever client sends request to this flow.
What attribute you would change in ClientRequestFlow to make this implementation work
successfully?
A. Change the method attribute value to "*’’
B. Change the path attribute value to "/api/ship"
C. Change the allowed method attributes value to "POST"
D. Change the protocol attribute value to "HTTPS"
Explanation:
Correct answer is Change the method attributes value to "POST".
It can be fixed in either of the two ways as below.
1) Changing method attribute to POST in ClientRequestFlow
2) Setting allowedMethods as PUT in ShippingFlow (but doesn't fit as question mentions
about changing ClientRequestFlow)
Refer to the exhibits.
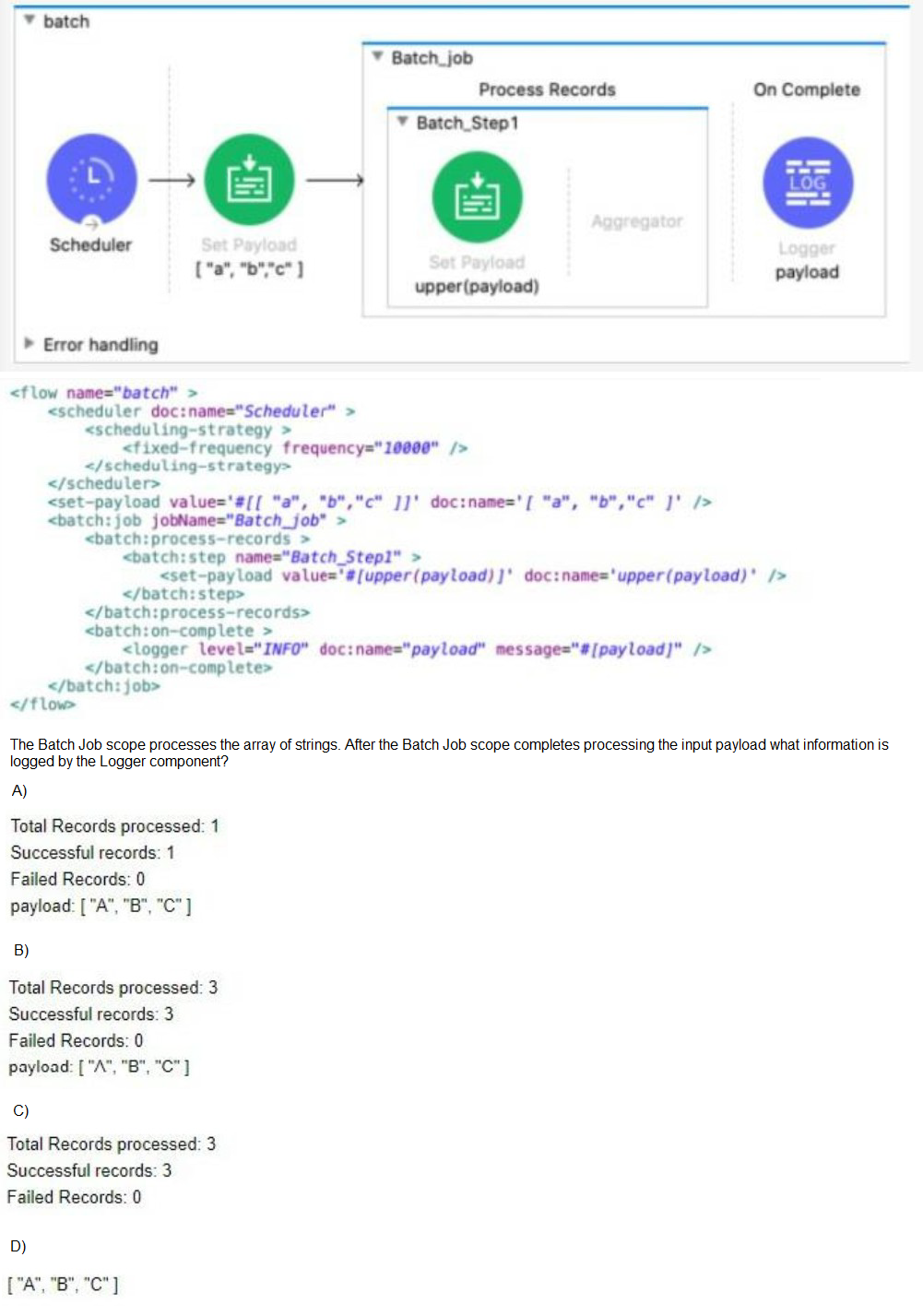
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Refer to the payload.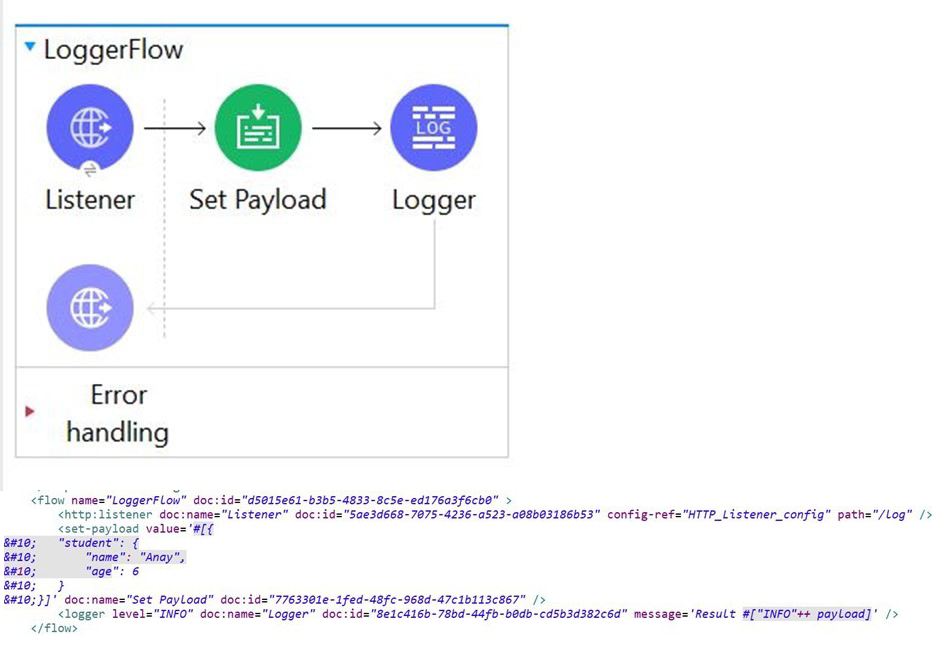
The Set payload transformer sets the payload to an object. The logger component's
message attribute is configured with the string "Result #["INFO"++ payload]"
What is the output of logger when this flow executes?
A. Result INFOpayload
B. Result INFO{"student":{"name":"Anay","age":6}}
C. 1. 1. "You called the function '++' with these arguments:
2. 2. 1: String ("INFO")
3. 3: Object ({student: {name: "Anay" as String {class: "java.lang.String"},age: 6 as
Numbe...)
D. Error : You evaluated inline expression # without ++
Explanation:
Correct answer is as below as concatenation operation works only with string and not with
the objects. In this case payload is object.
"You called the function '++' with these arguments:
1: String ("INFO")
2: Object ({student: {name: "Anay" as String {class: "java.lang.String"},age
| Page 5 out of 29 Pages |
| Mulesoft MCD-Level-1 Exam Questions Home | Previous |