What happens to the attributes of a Mule event in a flow after an outbound HTTP Request is made?
A. Attributes are replaced with new attributes from the HTTP Request response (which might be null)
B. New attributes may be added from the HTTP response headers, but no headers are ever removed
C. Attributes do not change
D. Previous attributes are passed unchanged
Explanation:
Attributes are replaced with new attributes from the HTTP Request response.
Attributes include everything apart from Payload/body. For ex: Headers, query parameters,
URI parameters.
So, when outbound HTTP request is made, new attributes need to pass the outbound
HTTP request and old attributes are replaced.
I have created below diagram to make it easy for you to understand: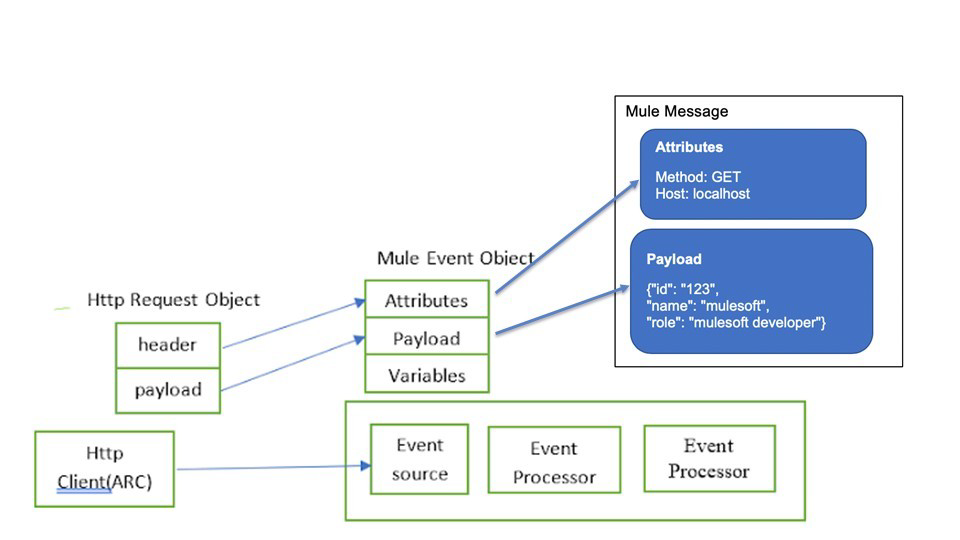
Refer to the exhibits.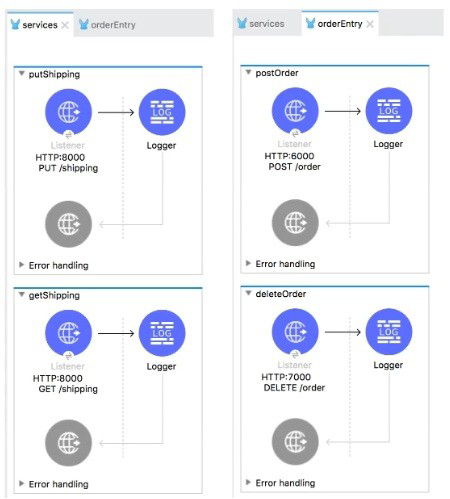
The two Mule configuration files belong to the same Mule project. Each HTTP Listener is
configured with the same host string and the port number, path, and operation values are
shown in the display names.
What is the minimum number of global elements that must be defined to support all these
HTTP Listeners?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Explanation:
In this case three configurations will be required each for port 8000, 6000 and 7000.
There would be three global elements defined for HTTP connections.
Each HTTP connection will have host and port. One example shown below with host as localhost and port 6000.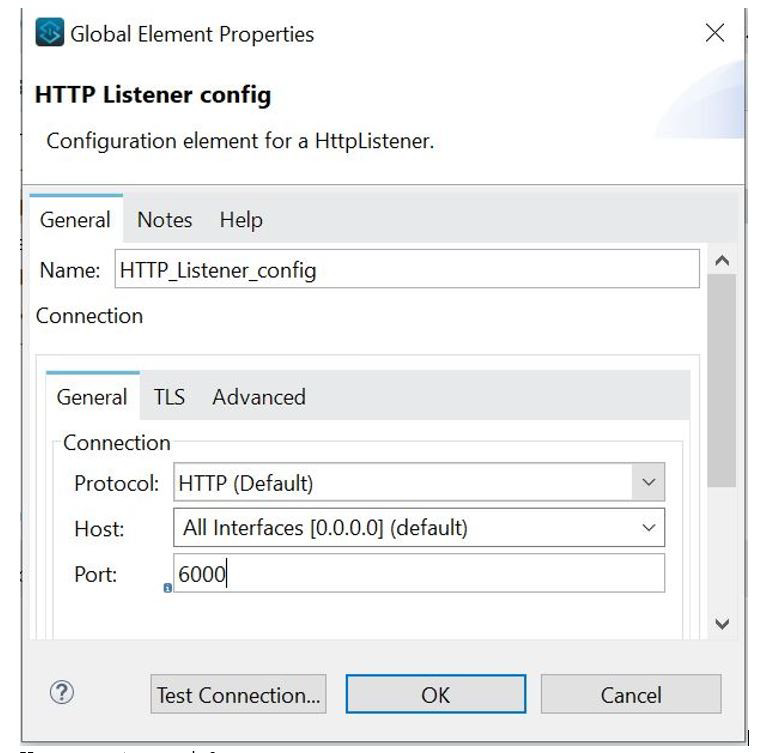
In an application network. If the implementation but not the interface of a product API
changes, what needs to be done to the other APIs that consume the product API?
A.
The applicationsassociated with the other APIs must be restarted
B.
The applications associated with the other APIs must be recoded
C.
The other APIs must be updated to consume the updated product API
D.
Nothing needs to be changed in the other APIs or their associated applications
Nothing needs to be changed in the other APIs or their associated applications
A web client submits a request tohttp://localhost:8081/books/0471767840. The value
"0471767840" is captured by a Set Variable transformer to a variable named booklSBN.
What is the DataWeave expression to access booklSBN later in the flow?
A.
booklSBN
B.
attributes.booklSBN
C.
flowVars.booklSBN
D.
vars. booklSBN
vars. booklSBN
In the execution of scatter gather, the "sleep 2 sec" Flow Reference takes about 2 sec to complete, and the "sleep 8 sec" Flow Reference takes about 8 sec to complete. About how many sec does it take from the Scatter-Gather is called until the "Set Payload" transformer is called?
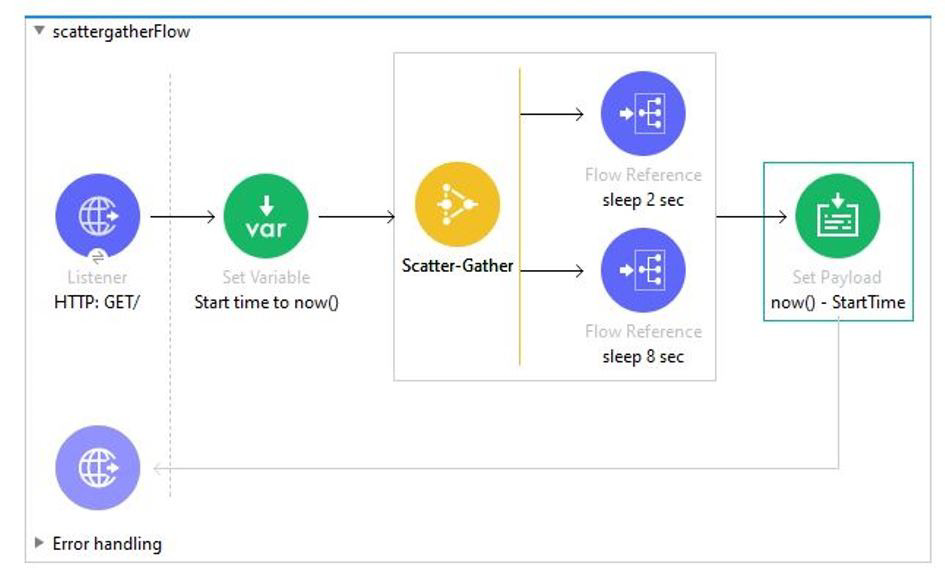
A. 8
B. 0
C. 2
D. 10
Refer to the exhibits.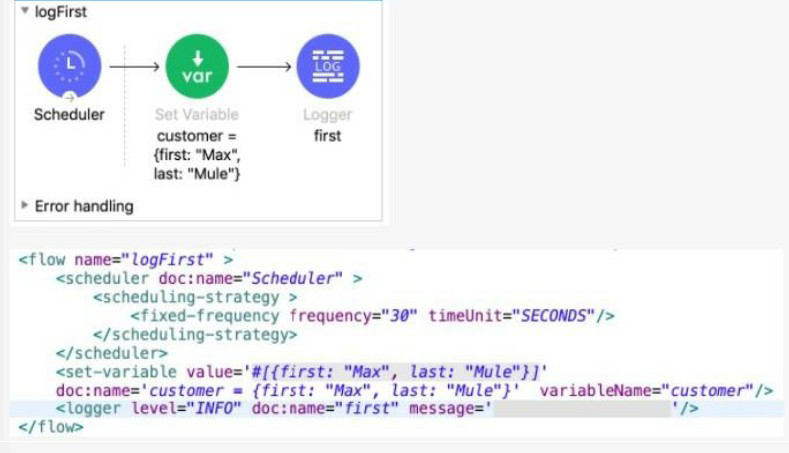
The Set Variable transformer is set with value #[ [ first "Max" last "Mule"} ].
What is a valid DataWeave expression to set as the message attribute of the Logger to
access the value "Max" from the Mule event?
A. vars "customer first"
B. "customer first"
C. customer first
D. vars "customer" "first"
Which file is used to define the interface contract to invoke a web service implemented as a SOAP service?
A. RAML
B. WSDL
C. JSON
D. OAS
WSDL is used to define the contract in case of SOAP . RAML/OAS is used to REST services.
Refer to the exhibits.
A web client sends sale data in a POST request to the Mule application. The Transform
Message component then enrich the payload by prepending a vendor name to the sale data.
What is written to the sales.csv file when the flow executes?
A. The enriched payload in JSON format
B. The enriched payload in XML format
C. The enriched payload in CSV format
D. An error message
| Page 4 out of 29 Pages |
| Mulesoft MCD-Level-1 Exam Questions Home | Previous |