Which of the below is used by Mule application to manage dependencies which make sharing the projects lightweight and easier?
A. Configuration file
B. Global element
C. POM.xml
D. Cloudhub
POM.xml contains info about the project and configuration details used by Maven to build the project.
A RAML specification is defined to manage customers with a unique identifier for each
customer record. What URI does MuleSoft recommend to uniquely access the customer
identified with the unique ID 1234?
A.
/customers?custid=true&custid=1234
B.
/customers/1234
C.
/customers/custid=1234
D.
/customers?operation=get&custid=1234
/customers/1234
Refer to the exhibits.
A. *[order,customer]/status
B. */status
C. ?[order,customer]/status
D. *status
What HTTP method in a RESTful web service is typically used to completely replace an existing resource?
A. GET
B. PATCH
C. PUT
D. POST
PUT replaces the original version of the resource, whereas the PATCH method supplies a set of instructions to modify the resource.
What is the correct syntax for a Logger component to output a message with the contents
of a 3SON Object payload?
A.
The payload is: $(payload)
B.
#["The payload is: " ++ payload]
C.
The payload is: #[payload]
D.
#["The payload is: " + payload]
#["The payload is: " ++ payload]
A flow needs to combine and return data from two different data sources. It contains a
Database SELECT operation followed by an HTTP Request operation.
What is the method to capture both payloads so the payload from the second request does
not overwrite that fromthe first?
A.
Put the Database SELECT operation inside a Cache scope
B.
Put the Database SELECT operation inside a Message Enricher scope
C.
Nothing, previous payloads are combined into the next payload
D.
Save the payload from the Database SELECT operation to a variable
Save the payload from the Database SELECT operation to a variable
Refer to the exhibits 
What payload and quantity arelogged at the end of the main flow?
A.
[[1,2,3,4], 14]
B.
[[order1, order2, order3, order4], 14]
C.
[[1,2,3,4], 10]
D.
[orderlorder2order3order4,14]
[[1,2,3,4], 14]
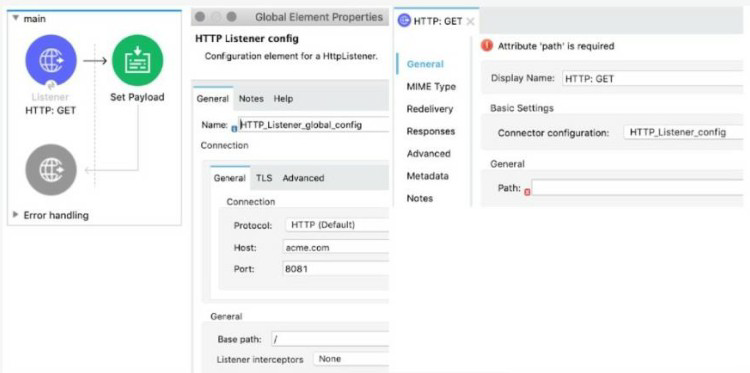
Refer to the exhibits. What payload is logged at the end of the main flow?
A.
[order1, order2, order3, order4]
B.
[1, 2, 3,4]
C.
order4
D.
order1order2order3order4
[1, 2, 3,4]
| Page 2 out of 29 Pages |
| Mulesoft MCD-Level-1 Exam Questions Home |