Which out of below is not an asset?
A. Template
B. Connector
C. Exchange
D. Example
Explanation:
Exchange is the odd man out here. Rest all are type of asset: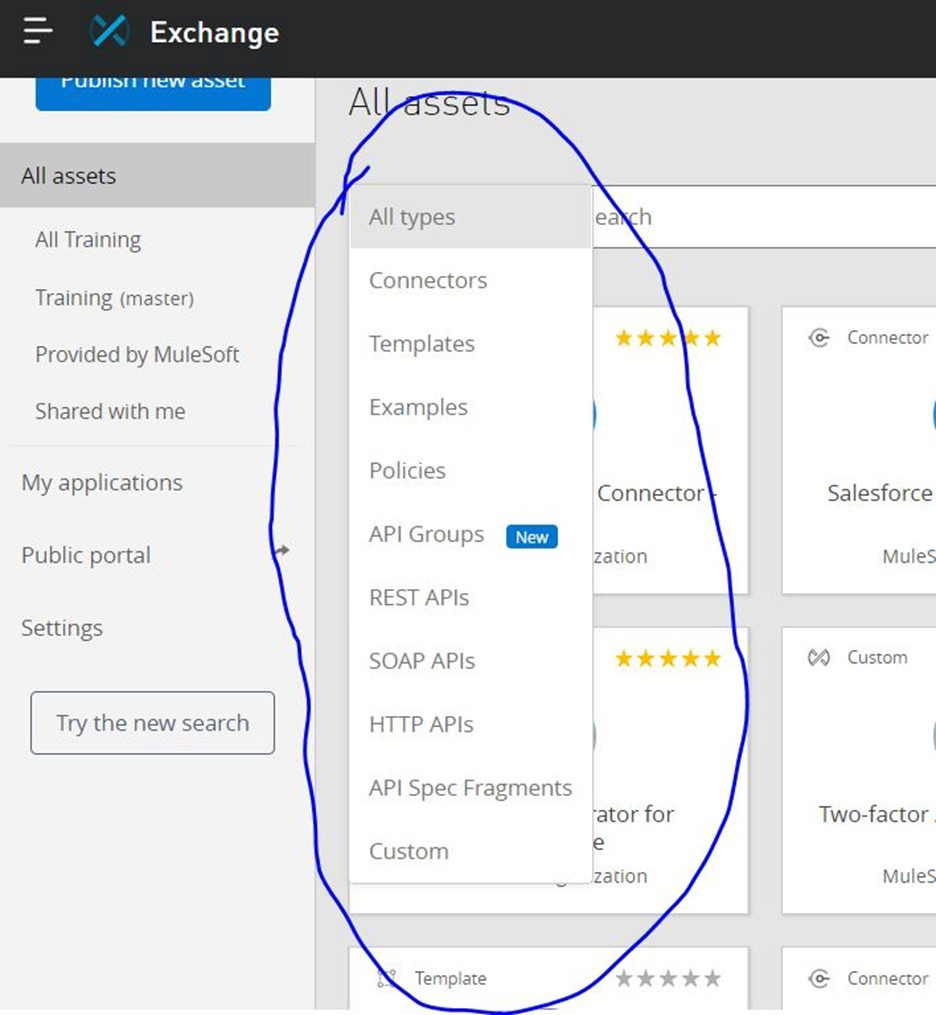
Refer to the exhibits. What payload is logged at the end of the main flow?
A.
[order1, order2, order3, order4]
B.
[1, 2, 3,4]
C.
order4
D.
order1order2order3order4
[1, 2, 3,4]
Refer to theexhibits.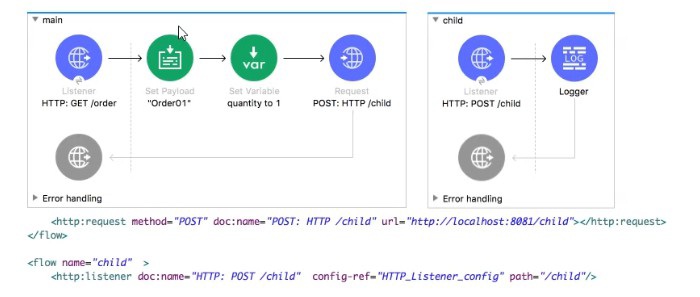
The main flow contains an HTTP Request. The HTTP Listeners and HTTP Request use
default configurations.
What values are accessible in the child flow after a web client submits a request to
http://localhost:8081/order? col or = red?
A.
payload
B.
payload
quantity var
C.
payload
color query param
D.
payload
quantity var color query param
payload
As a part of project requirement , you want to build an API for a legacy client. Legacy client can only consume SOAP webservices. Which type the interface documentation can be prepared to meet the requirement?
A. RAML file to define SOAP services
B. WSDL file
C. JSON file
D. plain text file documenting API's
Web Services Description Language. WSDL is used to describe SOAP based web services
Refer to the exhibit.
How many private flows does APIKIT generate from the RAML specification?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
What is the correct syntax todefine and call a function in Database? 
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option A
What of the below is not a feature of API Notebooks?
A. API documentation
B. Creates a client for an API
C. Creates a mock service for an API
D. Perform authenticated live calls on a real server
Explanation:
Correct answer is Creates a mock service for an API
API Notebook is an open source, shareable web application for API documentation,
interactive API tutorial and example generatation, and a client for your API endpoints.
Using API Notebook, you can make requests and quickly transform the responses into
readable format. However it cannot be used to mock service for an API.
Refer to the exhibit.
The main flow contains a Flow Reference for the child flow.
What values are accessible in the child flow after a webclient submits a request to
http://localhost:8Q81/order? color=red?
A.
payload
B.
payload
quantity var
C.
payload
color query param
D.
payload
quantity var color query param
payload
quantity var color query param
| Page 10 out of 29 Pages |
| Mulesoft MCD-Level-1 Exam Questions Home | Previous |